Published: 26 Nov 2010
Modified: 17 Feb 2025
Natura 2000 Protected
Nature territories cover 12 % (or 784 300 hectares) of the territory of Latvia. There are 327 Natura 2000 Protected Nature territories for the protection of habitats and species..
Latvia’s Specially Protected Nature Territories
and designated Natura 2000 sites occupy almost 19 % of its territory.
Seven Specially Protected Marine Territories have recently been established
and approved in Cabinet of Ministers Regulations
and are now accepted as a new category in Latvia’s
nature conservation system.
Figure 1 MAP
OF SPECIALLY PROTECTED NATURE TERRITORIES IN LATVIA
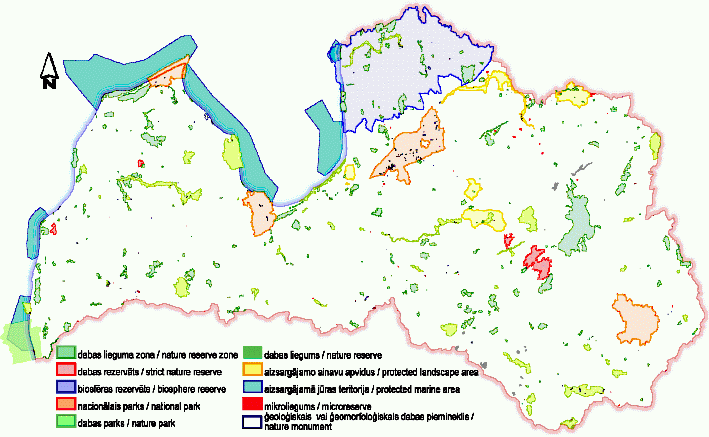
Source:
Nature Protection Agency of Latvia
SPECIALLY
PROTECTED NATURE TERRITORIES BY CATEGORY IN LATVIA
Figure 2. A. NATURA
2000 DESIGNATED AREAS BY CATEGORY (TOTAL: 327)
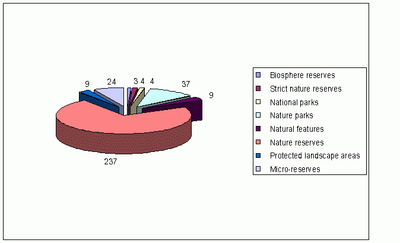
Figure 3. B. SPECIALLY PROTECTED NATURE TERRITORIES INCLUDING NATURA 2000 BY CATEGORY (TOTAL: 692)
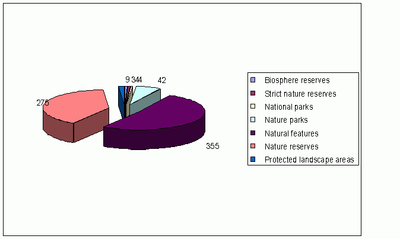
Source:
1. Ministry of Environment of Latvia
- http://www.vidm.gov.lv/eng/darbibas_veidi/specially_protected_nature_territories/
2. Nature Protection Agency of Latvia
- http://www.daba.gov.lv/index.php?objid=816
- http://www.daba.gov.lv/index.php?objid=959
There are 18 047
animal, 5 396 plant and 4 100 mushroom species in Latvia. Experts
consider 907 species (about 3.3 %) to be rare and endangered, while 723
plant and animal species and 93 biotopes have been included in lists of
specially protected species and habitats. The protection of species and
habitats is assured in Specially
Protected Nature Territories and at Natura 2000 sites and micro-reserves.
Figure 4
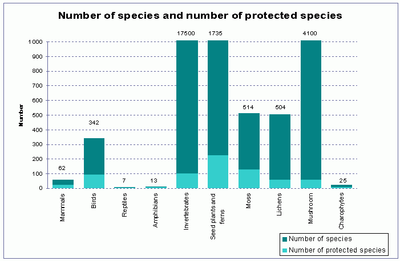
Table 1. NUMBER OF SPECIES AND NUMBER OF PROTECTED
SPECIES
Species and habitat management plans have been developed
and adopted for certain species. The plans contain information about species
distribution, significant areas requiring habitat protection, population of
species or tendencies, influential factors and planned measures to improve the condition
of the species or habitat. Endangered animals, plants and habitats are also protected
outside of the protected areas. For example, protection of the wild Baltic
salmon is one of a number of priority issues. Wetland
ecosystems also play an important role in maintaining both the climate and the
condition of water. Specific flora and fauna has developed in bogs and certain
species preserved there are relics of the last glacial period around 20 000
years ago. One way in which the conditions for biodiversity are improved is by converting
agricultural lands into natural areas when agricultural activity decreases.
The Nature
Conservation Agency of Latvia oversees the
implementation of nature protection policy in Latvia and maintains
a database (geographical location, quantitative and qualitative status) of
protected plants species, habitats and micro-reserves. However, the database on
habitats and species has been compiled on the basis of fragmentary research. More
modern data collection methods and methodological improvements are required to
improve efficiency in this area.
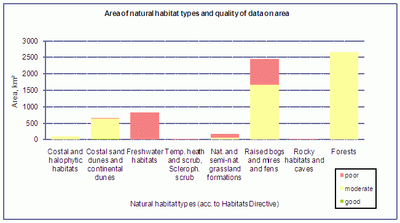
Table 2. AREA OF NATURAL HABITAT TYPES AND QUALITY OF
DATA ON AREA
|
Habitats
|
Quality of data on
area (km²)
|
|
|
good
|
moderate
|
poor
|
|
Costal and halophytic habitats
|
2
|
107
|
|
|
Costal sand dunes and continental dunes
|
14
|
609
|
1
|
|
Freshwater habitats
|
|
|
824
|
|
Temp. heath and scrub, scleroph. scrub
|
|
1
|
14
|
|
Nat. and semi-nat. grassland formations
|
|
73
|
87
|
|
Raised bogs, mires and fens
|
|
1650
|
808
|
|
Rocky habitats and caves
|
|
|
1
|
|
Forests
|
|
2643
|
|
Source: Nature Conservation Agency
Figure 5.
As a result of climate
change, a semi-enclosed sea structure and intensive
shipping, invasive alien species pose an increasing risk for the marine
ecosystems of the Baltic Sea.
Figure
6. FACT SHEETS ON INVASIVE ALIEN SPECIES
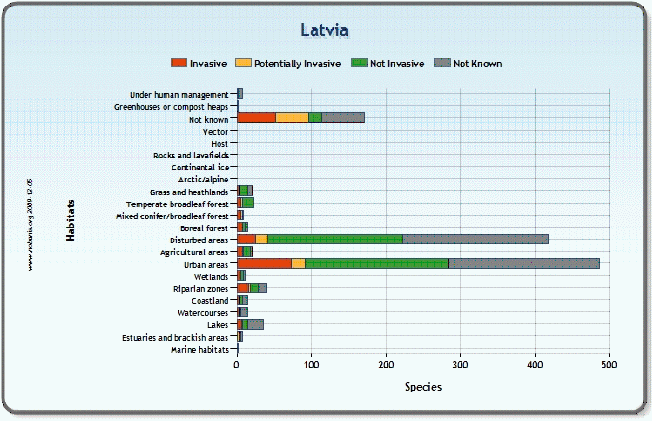
Source: The NOBANIS fact sheets http://www.nobanis.org/Charts.asp
Regulations of the Cabinet of Ministers of Latvia No.
17 (17.01.2010) “On Specially Protected Marine Territories”






Document Actions
Share with others