
Pollution changes a medium such as air, water or soil in a way that can make it harmful to people or
nature. Different types of pollutants include chemicals, dust, noise and radiation. EEA Signals 2020
looks at pollution through different lenses related to the Agency’s work and EU legislation.
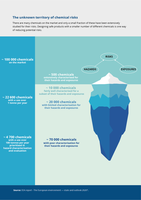
There are many chemicals on the market and only a small fraction of these have been extensively
studied for their risks. Designing safe products with a smaller number of different chemicals is one way
of reducing potential risks.
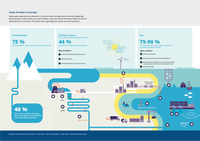
Waste water treatment and reductions in nutrient losses from agriculture have led to significant
improvements in water quality in Europe. However, many of Europe’s freshwater bodies are still not
doing well and the condition of Europe’s seas is generally poor, partly because of pollution.

Almost all Europeans who live in cities are exposed to air pollution that exceeds the levels set in the
World Health Organization’s (WHO’s) guidelines for clean air. Air pollution is the greatest environmental
health hazard in Europe and globally.
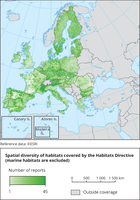
The map shows the number of terrestrial ART17 habitats reports per 10x10km GRID cells (2013-2018)

The map shows the biogeographical and marine Regions for EU28 countries.
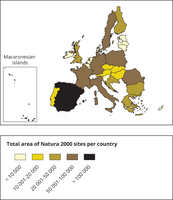
This map is a cartogram that distorts the geometry of regions to convey specific information by resizing. The bottom left box refers to the Macaronesian islands (Azores, Madeira and Canary Islands). It only includes terrestrial Natura 2000 sites for EU-28 (SPAs, SACs, SCIs and proposed SCIs).
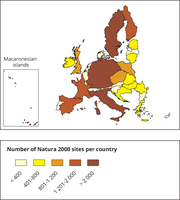
This map is a cartogram that distorts the geometry of regions to convey specific information by resizing. The box on the bottom left refers to the Macaronesian islands (Azores, Madeira and Canary Islands). It only includes terrestrial Natura 2000 sites for EU-28 (SPAs, SACs, SCIs and proposed SCIs).
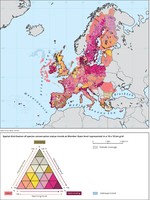
The map shows an index of conservation status trends of habitats calculated on a 10 x 10 km distribution grid

The map shows the biogeographical and marine regions for EU-28 countries.
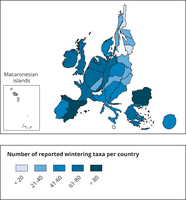
This map is a cartogram that distorts the geometry of regions to convey specific information by resizing. Here, the size of the country shows the number of reported species in relation to the country size. The map do not show all species appearing in a country. Thus, the map shows the reporting result rather than the species diversity of a country. The box on the bottom left refers to the Macaronesian islands (Azores, Madeira and Canary islands). Romania has not reported and is therefore not included in the map.

The overlap for Norway and Switzerland relates to Emerald Network sites. For all other countries the overlap relates to Natura 2000 sites. Statistics on national designations are based on data reported by EEA countries to the Nationally designated areas (CDDA) database.
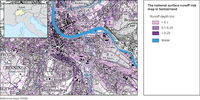
The map shows which regions of Switzerland are at risk from surface runoff and how deep they may be under water, as well as the anticipated flood paths of the water.
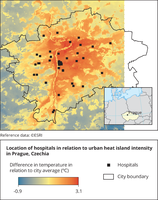
The map shows the location of hospitals in relation to urban heat island in Prague

The map shows the climate risk typology developed In the EU-funded H2020 project RESIN. The NUTS3 regions have been categorised into 8 groups according to the main climate hazards, exposure of population and infrastructure, sensitivity of the population and adaptive capacity of the areas.

The selection of cities comes from the source data. The P90 (90th percentile) indicator of the climatic suitability of the urban area for tiger mosquito represents the specific exposure of single cities and is independent of the model domain or size of a city. Since it is the 90th percentile, there are grid cells (areas) in a city with an even higher suitability value, so it can be considered a rather conservative value. For specific values for individual cities, see the Urban Adaptation Map Viewer.
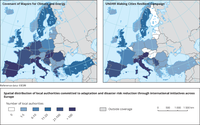
The map shows the number of local authorities per country that are signatories to the Covenant of Mayors (left map) or participate in the 'Making cities resilient' campaign by UNDRR (right map).

The maps show the spatial distribution of the European cities participating by the EU-funded research, implementation and knowledge exchange projects.
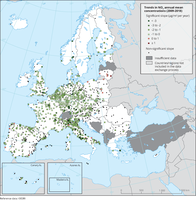
The map shows trend analysis considering NO2 annual mean observations at monitoring sites. The coloured squares represent stations with "significant" trends, while the black dots represent stations with “non-significant” trends.

The map shows trend analysis considering the ozone indicator AOT40 for vegetation calculated at monitoring sites. The coloured squares represent stations with "significant" trends, while the black dots represent stations with “non-significant” trends