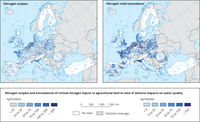
The map shows the calculated nitrogen surplus (inputs minus crop removal) and exceedance of critical nitrogen inputs to agricultural land in view of adverse impacts on water

This viewer presents selected emission factors and abatement efficiencies included in the EMEP/EEA Guidebook 2019. Information is ordered by the respective Nomenclature For Reporting (NFR) source category code. Not all emission factors included in the Guidebook are included in this viewer, users should always therefore consult the relevant chapter. In case of discrepancies between values appearing in this viewer and the published chapter, the values provided in the chapter are considered the official data.

Observed concentrations of benzene in 2017. The map shows the benzene annual mean concentrations. Dots in the last colour category indicate stations with exceedances of the annual limit value (5 µg/m3). Dots in the first colour category correspond to concentrations under the estimated WHO reference level (1.7 µg/m3). Only stations with more than 50 % of valid data have been included in the map.

Soil contains significant amounts of carbon and nitrogen, which can be released into the atmosphere depending on how we use the land. Clearing or planting forests, the melting of permafrost can tilt the greenhouse gas emission balance one way or the other. Climate change can also substantially alter what farmers can produce and where.

Soil plays a crucial role in nature’s cycles, including the nutrient cycle, which involves how much soil organic matter — i.e. carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus — is taken up and stored in soil. Organic compounds, such as leaves and root tips, are broken down to simpler compounds by organisms living in soil before they can be used by plants. Some soil bacteria convert atmospheric nitrogen into mineral nitrogen, which is essential for plant growth. Fertilisers introduce nitrogen and phosphates to induce plant growth but not all amounts are taken up by plants. The excess can enter rivers and lakes and affect life in these water ecosystems.

Europe's land and soil face a number of pressures, including urban expansion, contamination from
agriculture and industry, soil sealing, landscape fragmentation, low crop diversity, soil erosion and
extreme weather events linked to climate change.
Greener cities with cleaner energy and transport systems, a green infrastructure connecting green areas,
less intensive sustainable agricultural practices can help make Europe's land use more sustainable and
soils healthier.
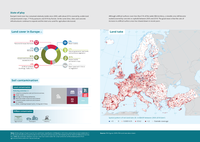
Europe’s land cover has remained relatively stable since 2000, with about 25 % covered by arable land
and permanent crops, 17 % by pastures and 34 % by forests. At the same time, cities and concrete
infrastructures continue to expand and the total area used for agriculture decreased.
Although artificial surfaces cover less than 5 % of the wider EEA territory, a sizeable area still became
sealed (covered by concrete or asphalt) between 2000 and 2018. The good news is that the rate of
increase in artificial surface areas has slowed down in recent years.



