
These maps show the relative change in maximum 100-year daily river discharge for two scenarios of global warming(1.5 °C and 3 °C)
The datasets below correspond to a new version of the Effective Mesh Density (seff) 2016 dataset with improved input data, for the years 2009, 2012 and 2015. This time-series uses the Copernicus Imperviousness and the TomTom TeleAtlas datasets as fragmenting geometries.
The Effective Mesh Density (seff) is a measure of the degree to which movement between different parts of the landscape is interrupted by a Fragmentation Geometry (FG). FGs are defined as the presence of impervious surfaces and traffic infrastructure, including medium sized roads. The more FGs fragment the landscape, the higher the effective mesh density hence the higher the fragmentation. An important consequence of landscape fragmentation is the increased isolation of ecosystem patches that breaks the structural connections and decreases resilience and ability of habitats to provide various ecosystem services. Fragmentation also influences human communities, agriculture, recreation and overall quality of life. Monitoring how fragmentation decreases landscape quality and changes the visual perception of landscapes provides information for policy measures that aim at improving ecosystem condition and restoration as well as maintaining the attractiveness of landscapes for recreational activities. The geographic coverage of the datasets is EEA39.
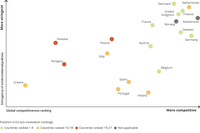
The figure includes all EEA member countries for which data are available on stringency of environmental policy. Countries are positioned according to their ranking in the WEF global competiveness index 2015 (x-axis) and the OECD stringency of environmental policy index (y-axis). The position of countries in the EU eco-innovation ranking are indicated using colours.

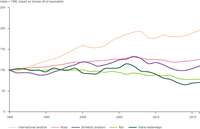
This figure presents the fuel efficiency and fuel consumption trends for private cars in the EU-28 in the period 1990 to 2015. The variables included are number of cars, average CO2 emissions of cars, average fuel consumption of cars, GDP, total distance travelled by cars and total energy consumptions of cars.
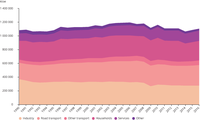
Energy consumption by transport mode
Final energy consumption by sector

SDGs interactions
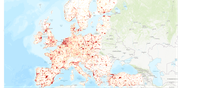
For visualisation purposes, the initial 100 m spatial resolution Corine Land Cover dataset was re-sampled to a 10 km2 grid. The observation periods can be visualised by activating the 'layers' icon and selecting the respective periods.
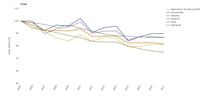

In 2015, on average, there were around 1.5 fragmented landscape elements per km 2 in the European Union [1] , a 3.7 % increase compared with 2009.
Approximately 1.13 million km 2 , around 28 % of the area of the EU [1] , was strongly fragmented i n 2015 , a 0.7 % increase compared with 2009.
There was less of an increase in fragmented landscape elements and in the area of strongly fragmented landscape between 2012 and 2015 than between 2009 and 2012 (1.4 and 0.18 percentage points, respectively).
Arable lands and permanent croplands (around 42 .6 %) and pastures and farmland mosaics (around 40.2 %) were most affected by strong fragmentation pressure in 2015 in the EU. Between 2009 and 2015, however, the largest increase in the area of strongly fragmented landscape was in grasslands/pastures and in farmland mosaics.
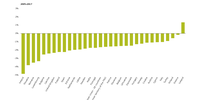
Luxembourg (91 %), Belgium (83 %) and Malta (70 %) had the largest proportions of strongly fragmented landscape in 2015 (as a proportion of their country area). The Baltic countries and Finland and Sweden were on average the least fragmented countries in the EU.
Between 2009 and 2015, the area of strongly fragmented landscape increased most in Croatia, as well as in Greece, Hungary and Poland.
[1] Romania is excluded because of the poor coverage of fragmentation geometry data in 2009.
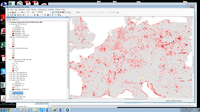
This web map application uses the new version of the Effective Mesh Density (seff) 2016 dataset with improved input data, for the years 2009, 2012 and 2015. This new dataset uses the Copernicus Imperviousness and the TomTom TeleAtlas data sets as fragmenting geometries. The application shows the change in effective mesh density (seff), i.e. the number of landscape elements between 2009 and 2012 and between 2012 and 2015.

The figure shows non-binding environmental objectives and binding environmental targets for the EU-28 as a whole in the period 2015-2050. Each objective/target is shown for the year of its implementation deadline.

Comparison of GHG emissions with 1990 levels (1990 = 100 %)

The graph shows the development of the Gross Nitrogen Balance (GNB) (kg nutrient/ ha Utilised Agricultural Area (UAA)) for the EU 28 over the period from 2004 to 2015, together with the nitrogen use efficiency (NUE) and GVA of the agricultural industry (values at current prices). For displaying all thre parameters and the development of their trends, an index is used setting 2005-values = 1
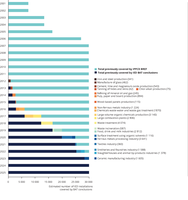
Estimated number of IED installations covered by BAT conclusions
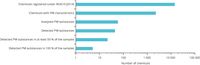
Note: Logarithmic scale; PM: substances that are Persistent and Mobile.

Total pollutant emissions to water and transfers to UWWTPs by industry from 2007 to 2017 by pollutant group

Key industrial air pollutant and GHG emissions for EEA-33 in 2007 to 2016 by industry sector