
The dots represent measurements stations, where the changes have been estimated using UTD monitoring data and the generalized additive model (GAM). The background shading represents the changes estimated using CAMS chemical transport modelling with an emission inventory estimated for the lockdown conditions.

The dots represent measurements stations, where the changes have been estimated using UTD monitoring data and the generalized additive model (GAM). The background shading represents the changes estimated using CAMS chemical transport modelling with an emission inventory estimated for the lockdown conditions
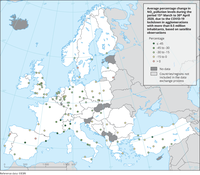
The map shows the average percentage change in NO2 pollution levels from NO2 TROPOMI satellite observations during the period 15th March to 30th April, comparing the observations under the COVID-19 lockdown to the business-as-usual scenario, in European agglomerations with more than half a million inhabitants. The gradient boosting regressor machine learning technique was used to simulate a business as usual (BAU) NO2 tropospheric columns satellite observations.

Relative reductions by country, in 2018 compared to 2009, in the estimated premature deaths (PD) attributed to exposure to PM2.5.
All Member States are requested by the Birds Directive to monitor bird species and send a report every 6 years following an agreed format. This information includes population sizes and trends (short and long term) for breeding and wintering populations, as well as pressures and threats for Special Protection Area trigger species. In addition, population status and trends are assessed at the EU level.
All Member States are requested by the Habitats Directive to monitor habitat types and species listed in its annexes and send a report every 6 years following an agreed format. The assessment of conservation status is based on information about the status and trends of species populations and of habitats at the level of the biogeographical or marine region.
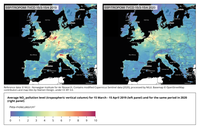
The figure shows the average NO2 pollution level (tropospheric vertical column) from Sentinel-5P/TROPOMI for the period 15 March to 15 April 2019 and for the same period in 2020.

The pan-European High-Resolution Snow & Ice products (HR-S&I) are provided at high spatial resolution (20 m x 20 m), and are derived from the Sentinel-2 constellation data (Sentinel-2A and Sentinel-2B: revisit time 5 of days). They are generated over the entire EEA38 +UK from September 1, 2016 onwards.

New technology and tools are opening up new possibilities for environmental monitoring and analysis. For
example, citizen science, satellite observations, big data and artificial intelligence present opportunities for
improving the timeliness, comparability, granularity and integration of data.

Noise pollution is a growing environmental concern. Noise disturbs sleep and makes it harder to
learn in school. It can also cause or aggravate many health problems. The most important source of
environmental noise in Europe is road traffic.

Plastics have brought many benefits to our daily lives but the problem is that these products never truly
disappear. Therefore, we should perhaps think about plastics as a type of pollutant from the point of
their production and prevent plastic products and waste from leaking into the environment.
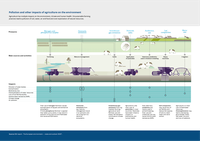
Agriculture has multiple impacts on the environment, climate and human health. Unsustainable farming
practices lead to pollution of soil, water, air and food and over-exploitation of natural resources.
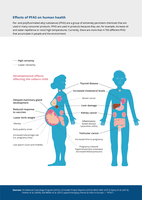
Per- and polyfluorinated alkyl substances (PFAS) are a group of extremely persistent chemicals that are
used in many consumer products. PFAS are used in products because they can, for example, increase oil
and water repellence or resist high temperatures. Currently, there are more than 4 700 different PFAS
that accumulate in people and the environment.

Pollution changes a medium such as air, water or soil in a way that can make it harmful to people or
nature. Different types of pollutants include chemicals, dust, noise and radiation. EEA Signals 2020
looks at pollution through different lenses related to the Agency’s work and EU legislation.
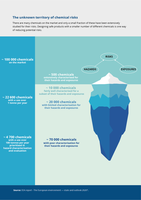
There are many chemicals on the market and only a small fraction of these have been extensively
studied for their risks. Designing safe products with a smaller number of different chemicals is one way
of reducing potential risks.
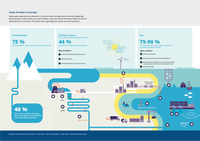
Waste water treatment and reductions in nutrient losses from agriculture have led to significant
improvements in water quality in Europe. However, many of Europe’s freshwater bodies are still not
doing well and the condition of Europe’s seas is generally poor, partly because of pollution.

Almost all Europeans who live in cities are exposed to air pollution that exceeds the levels set in the
World Health Organization’s (WHO’s) guidelines for clean air. Air pollution is the greatest environmental
health hazard in Europe and globally.
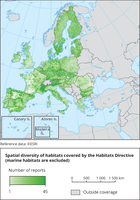
The map shows the number of terrestrial ART17 habitats reports per 10x10km GRID cells (2013-2018)

The map shows the biogeographical and marine Regions for EU28 countries.
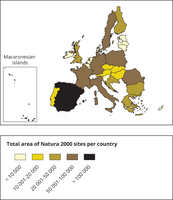
This map is a cartogram that distorts the geometry of regions to convey specific information by resizing. The bottom left box refers to the Macaronesian islands (Azores, Madeira and Canary Islands). It only includes terrestrial Natura 2000 sites for EU-28 (SPAs, SACs, SCIs and proposed SCIs).