
The quietness suitability index (QSI) provides the overview with the highest (QSI=1) and lowest (QSI=0) proportion of potential quiet areas in Europe.
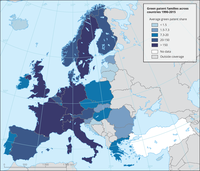
The map shows the quintiles of the geographical distribution of green patent families at country level.
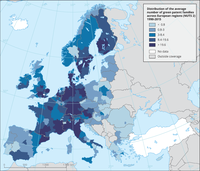
The map shows the quintiles of the geographical distribution of green patent families at regional level
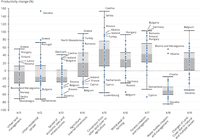
The chart shows the vegetation productivity changes (%) over areas with land use change in the period 2000-2018. The values are broken down by major land use change drivers.

Change of vegetation productivity during the years 2000-2016. Vegetation productivity was calculated for each 500m grid cell from a remote sensing derived vegetation index (PPI). The layer shows the changes expressed in % of 2000 calculated from the fitted line of the linear trend model.
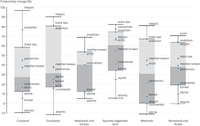
The chart shows significant trends of vegetation productivity, expressed in % change. The % change values were derived from the fitted linear trend line.

The chart shows the effect of frost frequency variations on vegetation productivity, expressed in standard deviation units of vegetation productivity.

The chart shows the effect of temperature variations on vegetation productivity, expressed in standard deviation units of vegetation productivity.
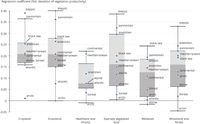
The chart shows the effect of precipitation variations on vegetation productivity, expressed in standard deviation units of vegetation productivity.

Vegetation productivity indicates the spatial distribution and change of the vegetation cover - a key characteristic of ecosystem condition.
Vegetation productivity in Europe on average has a regional pattern of increase and decline. Increase was observed most in South Eastern Europe, over croplands and wetlands in the Steppic region and grasslands and sparsely vegetated lands and in the Black Sea and Anatolian regions. Decline happened most over croplands and grasslands in the Atlantic region as well as over wetlands in the Alpine region.
Climate has important influence on vegetation productivity in Europe. Strongest driver is precipitation, especially in the South Eastern regions. Decreasing number of frost days increased productivity in the Pannonian region but decreased productivity in the Atlantic region.
Climatic variations are important drivers of vegetation productivity, but land use changes are even stronger. Productivity was most increased by agricultural land management and converting other lands to agriculture, whereas largest decrease was caused by sprawling urban areas.

This viewer provides statistics on spatial extent and land use distribution of floodplain areas of Europe. Here, floodplains are defined as the flood prone area, i.e. the area that would be flooded during a 100-year flood, if there were no flood protection in place. Most flood prone areas are, however, protected against flooding. The statistics are presented in a series of dashboards providing an overview of floodplain characteristics, by country, by river basin districts, and in Natura 2000 sites. The statistics include the extent of floodplains, their ecosystem distribution based on MAES classification and the Copernicus Riparian Zone Products, as well as land cover flows between 2000 and 2018.

This figure shows connectivity of rivers in EEA-39 as defined in "Mapping the world’s free-flowing rivers" (https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-019-1111-9). Dams and reservoirs and their up- and downstream propagation of fragmentation and flow regulation are the leading contributors to the loss of river connectivity.

The figure illustrates the estimated effects on national GHG emissions due to the increase in national renewable energy consumption since 2005

The figure illustrates the estimated effects on key air pollutants at the national level, following the increase in renewable energy consumption since 2005
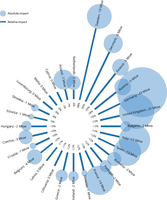
The figure illustrates the estimated effects on national primary energy use of fossil fuels due to the increase in national renewable energy consumption since 2005.

The figure illustrates how much renewable energy consumption has grown per technology and sector by 2018, compared with the corresponding levels in 2005 (EU-28).
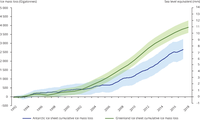
The figure shows the cumulative ice mass loss from the Greenland and Antarctic ice sheets from recent studies, weighted according to the primary satellite data source following the approach of the Ice Sheet Mass Balance Inter-comparison Exercise (The IMBIE team, 2018, doi:10.1038/s41586-018-0179-y; The IMBIE team, 2019, doi:10.1038/s41586-019-1855-2). The shaded uncertainty intervals are estimated from the standard deviation of the individual studies.

Input of impulsive anthropogenic sound was created by combining pulse-block-days (PBD) data from the ICES Registry (for HELCOM and OSPAR areas) and ACCOMBAS (for the Mediterranean Sea).
Electricity generation gives rise to negative impacts on the environment and human health throughout all stages of its life-cycle. To date, power generation remains the largest GHG-emitting sector in Europe. Carbon dioxide (CO2) is by far the most commonly-emitted GHG across the sector, being a product of combustion processes. An almost complete decarbonisation of the EU’s electricity sector is needed in order to meet the EU’s objective of becoming the first carbon-neutral continent by 2050.
Electricity can play an increasing role in decarbonising energy use across a number of sectors, such as transport, industry and households. Information about the carbon intensity of electricity generation is therefore relevant for many stakeholders. The EEA and its European Topic Centre for Climate Change Mitigation and Energy (ETC/CME) produce each year country- and EU-level data on the average annual CO2 emission intensity of electricity generation.

These maps present a story about how Europe might be affected by key climate hazards such as droughts, floods, forest fires and sea level rise during the 21st century and beyond. These maps are based on different greenhouse gas emissions scenarios and climate models and have been published already in various EEA reports and indicators.