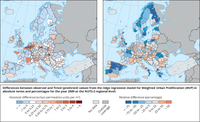
Differences between observed and fitted (predicted) values from the ridge regression model for Weighted Urban Proliferation (WUP) in absolute terms and percentages for the year 2009 at the NUTS-2 regional level.
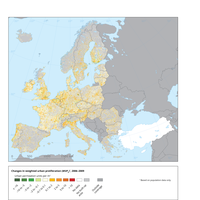
Changes in WUP at the scale of the 1-km2 grid between 2006 and 2009

Densification plan from the Canton of Zurich

The map shows the index of suitable quiet areas across Europe combined with the Natura2000 protected areas
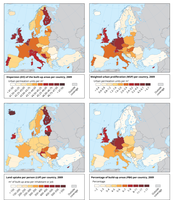
The maps shows urban sprawl per country for the four metrics WUP (Weighted Urban Proliferation), Urban Permeation (UP), Dispersion (DIS), and Land Uptake per Person (LUP) at the country level for Europe in the year 2009.

Maps of absolute and relative changes in the values of WUP in the NUTS-2 regions between 2006 and 2009.
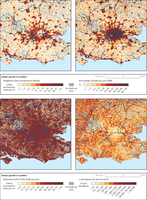
Urban sprawl in London at the 1-km2 scale in 2009 for:
Weighted urban proliferation (WUPp),
Percentage of build-up area (PBA),
Dispersion (DIS) of the built-up areas and
Land-uptake per person (LUP)

Transport demand is closely linked to economic activity: in periods of growth, economic output goes up, more goods are transported and more people travel. The impacts of transport on human health, the environment and climate change are closely linked to the choice of fuel. Clean alternative fuels, including electricity, are already available and can constitute viable options to petrol and diesel. Trip length plays a role in determining the suitability of the fuel type.
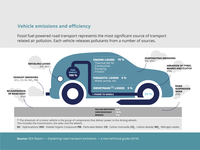
Fossil fuel powered road transport represents the most significant source of transport related air pollution. Each vehicle releases pollutants from a number of sources.

Many Europeans are exposed to harmful levels of air pollution. Up to 30 % of Europeans living in cities are exposed to air pollutant levels exceeding EU air quality standards. And around 98 % of Europeans living in cities are exposed to levels of air pollutants deemed damaging to health by the World Health Organization’s more stringent guidelines.

Noise pollution is a growing environmental concern, arising from a number of sources. The adverse effects of noise pollution can be found in the well- being of exposed human populations, in the health and distribution of wildlife, as well as in the abilities of children to learn at school.

Several EU targets have been set to reduce the environmental impacts of transport in Europe, including its greenhouse gas. The transport sector’s targets are part of the EU’s overall goal to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by 80 – 95 % by 2050.

Pollution events are more likely to occur under temperature inversion conditions. During extended periods of high pressure in winter months, solar radiation reaches the ground, warming it up. At night, the lack of cloud cover means the ground loses heat rapidly and the air in contact with the ground becomes colder. The warmer air rises and acts as a lid trapping the colder air close to the ground. Pollution, including that from road traffic is also trapped, so the air layer closest to the ground becomes more and more polluted. This continues until the prevailing meteorological conditions change.

EU progress in meeting emission ceilings (for compliance and for environmental objectives) of the four main air pollutants regulated in the 2001 National Emission Ceilings Directive





