All official European Union website addresses are in the europa.eu domain.
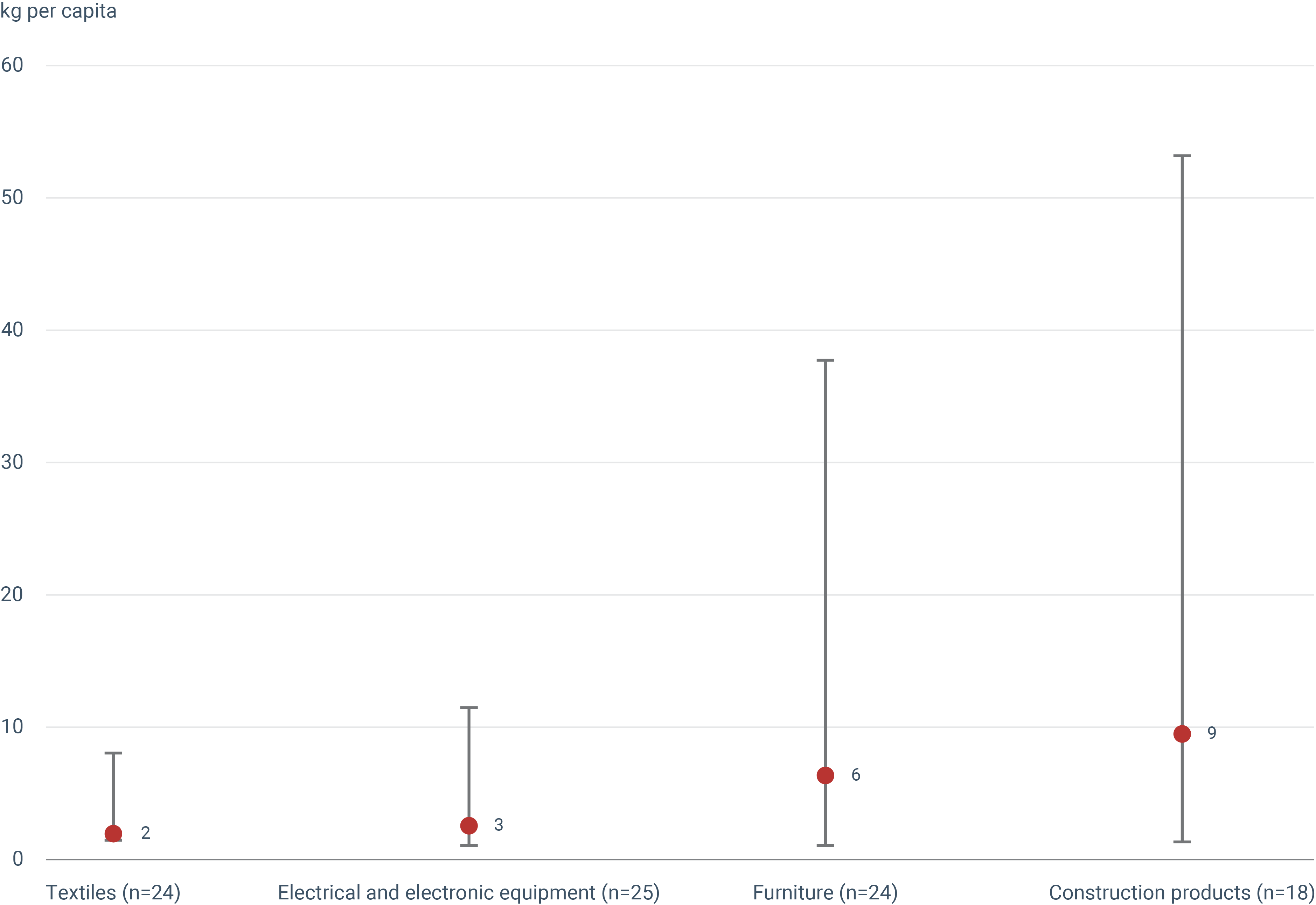
See all EU institutions and bodiesReported data on actual reuse in the EU show large differences across product categories and countries. Construction products have the highest average reuse at 11 kg per capita, while textiles show the lowest at 2 kg per capita.
In 2023, the first year of mandatory reporting, Member States submitted quantitative data on actual reuse, using 2021 as the reference year. The graph above presents the ranges across reporting countries for four categories: textiles, electrical and electronic equipment (EEE), furniture, and construction products and materials. Notably, reported data for furniture and construction products show wide variation, reflecting significant differences in reuse practices and methodologies for data collection across Member States. In contrast, reported values for textiles are more consistent, indicating less variation. Construction products and materials display the highest average reuse, at 11 kg per capita, while textiles have the lowest, at 2 kg per capita. These differences partly reflect the varying size and weight of products within each category. Possibilities for inter-country comparisons and further analysis remain limited due to the early stage of reporting and the associated uncertainties.
In 2021, average municipal solid waste (MSW) generation in the EU was 532 kg per capita, with approximately half of this amount (265 kg per capita) recycled. Early data on reuse, although limited, show considerable variation across the 20–21 Member States that reported reuse data. Reported figures indicate an average reuse of 13 kg per capita for categories relevant to MSW (textiles, EEE, and furniture), with values ranging up to 56 kg per capita (EEA, 2024f). Despite the uncertainties surrounding reuse data, even the highest reported levels remain significantly lower than per capita recycling rates. Despite increasing policy attention on waste prevention and continued growth in value added from circular economy activities, recycling continues to far exceed prevention activities such as reuse.
Policies promoting repair and reuse are among the most frequently prioritised in Member States’ Waste Prevention Programmes (WPPs). The policies encouraging reuse and repair included in all WPPs. Instruments in support of reuse and repair are predominantly soft measures, accounting for 83% of all instruments reported under this policy.
Continue browsing in the Circularity Metric Lab by visiting one of these thematic modules: