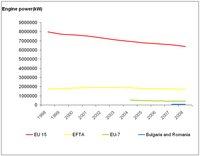
The figure shows changes in the power of the European fishing fleet. Countries have been grouped into the following categories: EU15 - Belgium, Denmark, Germany, Greece, Spain, France, Ireland, Italy, Luxembourg, Netherlands, Austria, Portugal, Finland, Sweden, United Kingdom; EFTA: Iceland, Norway; EU7 - Estonia, Cyprus, Lithuania, Latvia, Malta, Poland and Slovenia; and Bulgaria and Romania

The figure shows the state of commercial fish stocks in the Mediterranean Sea. Status of fish stocks was assessed from 2001-2009 in the GFCM regions, although data refers to 2005.
Year in the cells refer to year of ICCAT or GFCM assessments.
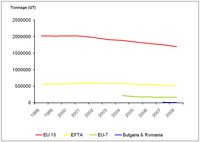
The figure shows changes in the tonnage of the European fishing fleet. Countries have been grouped into the following categories: EU15 - Belgium, Denmark, Germany, Greece, Spain, France, Ireland, Italy, Luxembourg, Netherlands, Austria, Portugal, Finland, Sweden, United Kingdom; EFTA - Iceland, Norway; EU7 - Estonia, Cyprus, Lithuania, Latvia, Malta, Poland and Slovenia; and Bulgaria and Romania.

The figure shows the state of commercial fish stocks in North East Atlantic and Baltic Sea. Status of fish stocks was assessed in 2009 in the ICES regions , although data refers to 2008.
Elasmobranchs not included as they constitute only about 3% of the total catch in the NE Atlantic and consist of many species and stocks which would mask the general trend.
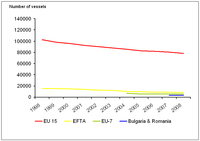
The figure shows the changes in the number of vessels of the European fishing fleet. Countries have been grouped into the following categories: EU15 - Belgium, Denmark, Germany, Greece, Spain, France, Ireland, Italy, Luxembourg, Netherlands, Austria, Portugal, Finland, Sweden, United Kingdom; EFTA - Iceland, Norway; EU7 - Estonia, Cyprus, Lithuania, Latvia, Malta, Poland and Slovenia; and Bulgaria and Romania

The figure shows changes in fishing fleet capacity and size between 1998 and 2008 in EU15 and EFTA countries. Countries have been grouped into the following categories: EU15 - Belgium, Denmark, Germany, Greece, Spain, France, Ireland, Italy, Luxembourg, Netherlands, Austria, Portugal, Finland, Sweden, United Kingdom; EFTA - Iceland, Norway.
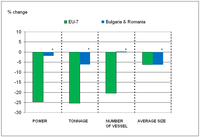
The figure shows changes in fishing fleet capacity and size between 2004 and 2008 for EU7 and 2007 and 2008 for Bulgaria and Romania. Countries have been grouped into the following categories: EU7 - Estonia, Cyprus, Lithuania, Latvia, Malta, Poland and Slovenia; and Bulgaria and Romania.

The graph shows the change in emissions of primary PM10 data, and emissions of PM2.5.

The graph shows the change in energy-related emissions of ozone precursors (NOx, NMVOC, CO and CH4) each weighted by an ozone formation factor prior to aggregation to represent their respective ozone forming potentials. The relative impact of the combined contribution of NOx, NMVOC, CO and CH4 to ozone formation can be assessed based on their tropospheric ozone forming potentials (TOFP): nitrogen oxides 1.22, non-methane volatile organic compounds 1.0, carbon monoxide 0.11 and methane 0.014 (de Leeuw 2002).

The figure shows the emission of NOx, NMVOC, CO and CH4 in 2008
Total gross inland energy consumption increased until 2004 in the EU-27It: it was about 10% above its 1990 level in 2004 (average growth of 0.7 % per year). Since 2004, it is has stopped growing: it was stable in 2005 and 2006 and decreased in 2007 and 2008 (by 1% and 0.5% respectively): as a result, the gross inland consumption was in 2008 1.4% below its 2004 level. Total gross inland energy consumption was in 2008 8.3% above its 1990 level.
Total gross inland energy consumption increased until 2004 in the EU-27It: it was about 10% above its 1990 level in 2004 (average growth of 0.7 % per year). Since 2004, it is has stopped growing: it was stable in 2005 and 2006 and decreased in 2007 and 2008 (by 1% and 0.5% respectively): as a result, the gross inland consumption was in 2008 1.4% below its 2004 level. Total gross inland energy consumption was in 2008 8.3% above its 1990 level.

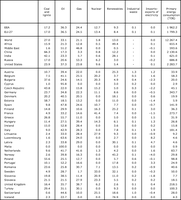
Share of RE (RE: renewable energy) in GEIC (GEIC: gross energy inland consumption), compared to target in COM(97) 599 final (%, in 2008). The White Paper on renewable energy (COM(97) 599 final) sets an indicative target of 12 % of renewables in total GEIC in the EU-15 by 2010. The contribution of renewable energy sources to GEIC in EU-15 was 8.6 % in 2008, falling significantly short of the 12% indicative target
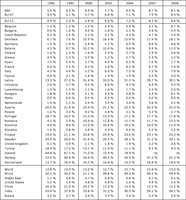
The table shows the share of renewable energy in total gross energy inland consumption (in %)
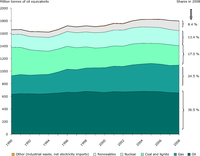
The figure shows the total primary energy consumption by energy source in 2008. The contribution of renewable energy sources to gross energy inland consumption (GEIC) increased in the EU-27 from 4.4 % in 1990 to 8.4 % in 2008. For the EU-15, the share of renewables in total gross inland consumption accounted for 8.6%, in 2008, falling substantially short of the indicative target set in the White Paper on renewable energy (COM(97) 599 final) of 12 % by 2010

The total electricity produced from natural gas increased by 592 TWh (274 %) between 1990 and 2008, at an annual average growth rate of 7.6 %. The primary motive for the switch to gas was economic, with low gas prices for much of the 1990s compared to coal and stricter environmental legislation. Because of this, significant investments were made in the transportation infrastructure for the delivery of gas from within and outside the EU-27. This rapid increased in gas demand also contributed to the increase in fossil fuels imports.

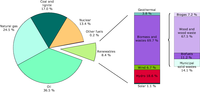
The figure shows the share of electricity production by fuel type in 2008.
Other fuels’ include electricity produced from power plants not accounted for elsewhere. such as those fuelled by certain types of industrial wastes. It also includes the electricity generated as a result of pumping in hydro-power stations. For Iceland no data for 2007-2008 were available from Eurostat, the 2006 data were used as an estimate.
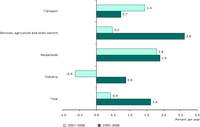
Since 1990, in the EU-27 the electricity consumption increased in the service sector (including agriculture) at an annual growth rate of 2.6 %. In total, the electricity consumption increased by 59.2 % between 1990 and 2008. The main reasons for increased electricity consumption in the service sector were the sustained growth of this sector throughout the EU, the increased use of electrical appliances (such as air conditioning, lighting or IT equipment) and the penetration of new electrical devices
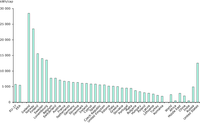
The average electricity use per capita in the EU-27 is over 2.3 times the global average and 2.8 times that of China. Only Luxembourg, Sweden, Finland, Norway and Iceland are using more electricity per capita than in the United States. The rest of the EU-27 is well below the US
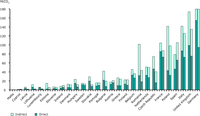
The figure shows the CO2 emissions in the industry in EU Countries