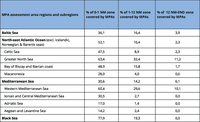
The table shows the percentage cover of MPAs and distance to 10% target for each regional and sub regional sea and by distance zone from the coastline modified from the report: Spatial analysis of Marine Protected Area Networks in Europe´s seas. EEA Technical report, no 17/2015
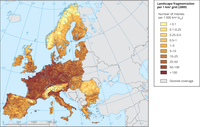
Map shows the patterns of fragmentation in the 29 countries investigated based on a grid of cells size of 1 km2
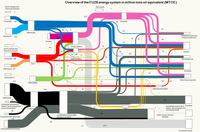
This Sankey diagram shows the composition of the primary energy entering the energy system of the EU-28 in 2013, and where this primary energy was used, either as losses or as consumption by specific sectors of the economy.
The units are million tonnes of oil equivalent (Mtoe).
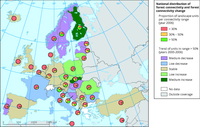
The map show the proportion of landscape units per connectivity range reported by country for the year 2006.
The trend (medium/low increase/decrease or stable) in the proportion of units in a high connectivity range (above 50%) is given for the period 2000-2006 per country.
Species dispersing is 1 km.
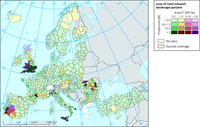
The map shows the spread of artificial and/or agricultural surfaces into previously ‘core natural/semi-natural’ landscapes for the period 2000-2006. Reporting is made per province (NUTS 2/3), both in terms of absolute area (ha) and proportionally to the ‘core natural’ pattern cover in 2000. For example, one province in the West of Spain had its ‘core natural’ pattern reduced by 1.5% to 3% due to fragmentation by agricultural and/or artificial lands, from a cumulative area of more than 10 000 ha.
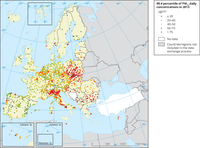
Observed air quality concentration maps for 2013 for components O3, PM10, NO2, PM2.5 and BaP.
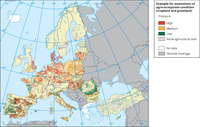
The map shows the condition of agro ecosystems map. Based on pan-European High Nature Value farmland map using as mask the agricultural categories of Corine land cover map of 2006.
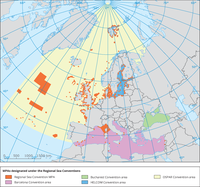
The map shows the different marine protected areas (MPA) designated under the Regional Sea Conventions
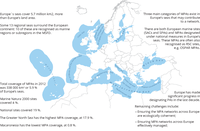
The map shows the facts on the EU Marine Protected Area Networks

The maps shows the regional seas surrounding Europe and the sustainability challenges they face
Soil is an important and often neglected element of the climate system. It is the second largest carbon store, or "sink", after the oceans. Restoring key ecosystems on land, and a sustainable use of the land in urban and rural areas, can help us mitigate and adapt to climate change.
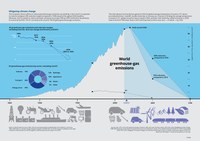
The European Union's effort to reduce greenhouse-gas emissions are working. In fact, the EU is expected to meet its unilateral 20 % reduction target (compared to 1990) ahead of the agreed 2020 deadline. Moreover, the EU intends to reduce domestic emissions by at least 40 % by 2030 and further decarbonise its economy by 2050. The EU currently emits around 10 % of global greenhouse-gas emissions.
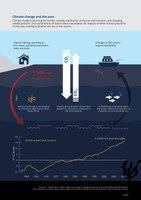
Climate change is warming the oceans, causing acidification of marine environments, and changing rainfall patterns. This combination of factors often exacerbates of other human pressures on the seas, leading to biodiversity loss in the oceans.


