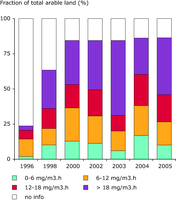
The target value for protection of vegetation is 18 (mg/m3).h while the long-term objective is set to 6 (mg/m3).h

The graph above shows the emissions of ozone precursors (methane CH4; carbon monoxide CO; nonmethane volatile organic compounds NMVOCs; and nitrogen oxides NOX) each weighted by a factor prior to aggregation to represent their respective tropospheric ozone formation potential (TOFP)
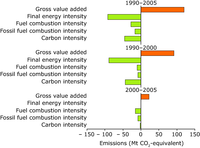
The orange bars show the factors that have an increasing effect on emissions and the green bars show the factors that have a reducing effect
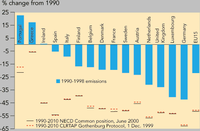
The targets for 2010 are the Gothenburg Protocol target (December 1999) and the more recent NECD Common Position targets (June 2000) for the EU and individual countries for non-methane volatile organic compounds and nitrogen oxides individually
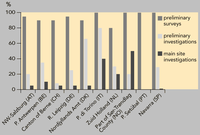
Information on remediation in progress and remediation completed has not been included.
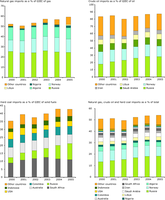
GIEC = gross inland energy consumption (or primary energy consumption).
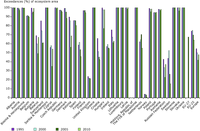
Data source of deposition-data used to calculate exceedances: EMEP/MSC-W
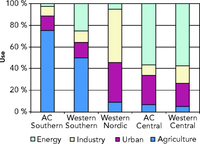
Southern accession countries (AC): Malta,Cyprus, Turkey

This graph shows new EU Member States Kyoto targets for 2008-2012.
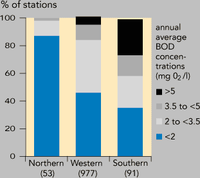
Northern: Finland (BOD7); Southern: Greece and Italy (BOD5); Western: Austria, Belgium, France, Ireland, Denmark, the Netherlands and the United Kingdom (BOD5)

Artificial and agricultural changes in and around the National Park
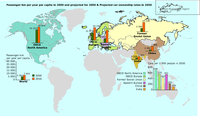
International comparison