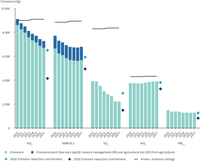
National Emission Ceilings Directive: Progress in meeting the 2010 emission ceilingsand the 2020 as well as 2030 reduction commitments.

Evolution of main air pollutant emissions and of the gross domestic product (GDP) in the EU-28; Values for 2000-2017 are expressed as percentage of 2000 levels. GDP is expressed in chain linked volumes (2010), as percentage of the 2000 level.
Methane (CH4) emissions are total emissions (Integrated Pollution Prevention and Control sectors 1-7) excluding sector 5: Land-use, land-use change and forestry. The present emission inventories include only anthropogenic non-methane volatile organic compound (NMVOC) emissions.

The solid line shows the development of primary energy consumption and final energy consumption. The dashed lines show the linear trajectories until 2030 and to the 2050 scenario results from the Commission's 2050 long term strategy.
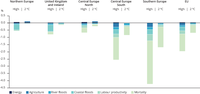
This figure 23 the welfare losses (as percentage of GDP) for the six sectoral impacts in
the five European regions and the EU-28 in both the high warming and the 2° C scenarios.
The EU welfare loss under the high warming scenario is estimated to be around 1.9% of
GDP (€240 bn) and could be reduced by approximately 2/3 in the 2° C scenario (€79 bn).
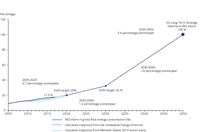
The solid line shows the development of the share of renewables in EU energy consumption based on historic data. The dashed lines show expected progress to 2020 based on projection data. The dots illustrate the 2020, 2030 targets.The 2050 scenario range illustrates the an average of eight scenarios published in the Commission's 2050 long term strategy.

EU part of the regional sea surface area (km2) and the area covered by MPAs in 2016 (dark colour and in %)

Economic damage caused by weather and climate-related extreme events
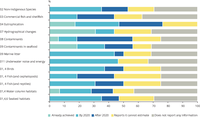
Timelines for achieving good environmental staus as reported by members states

Global average near surface temperature since the pre-industrial period

Drivers of GHG emission reductions from 1990 to 2017.
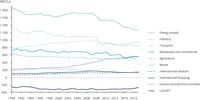
GHG emissions by main sector from 1990 to 2016.

Historic trends from 1990 to 2017 are represented in solid lines. Projections until 2035 are represented in dashed lines. The upper line represents the scenario "with existing measures", while the lower line represents the scenario "with additional measures". EU targets and objectives for 2020, 2030 and 2050 are represented as bullets.
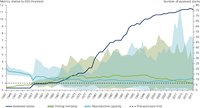
This figure shows trends in the status of assessed fish stocks between 1947 and 2017, expressed in two metrics: fishing mortality (F) and reproductive capacity (i.e. spawning stock biomass (SSB)). It reflects their average deviation relative to policy thresholds for Good Environmental Status (GES) (i.e. Fmsy and MSY B trigger respectively)*. For fishing mortality, 1 is a target (Fmsy), above which exploitation is unsustainable, while for reproductive capacity, 1 is a precautionary limit (MSY B trigger), below which there is a high risk that it is impaired.

Time series of annual average sea surface temperature (°C), referenced to the average temperature between 1993 and 2012, in the global ocean and in each of the European seas.

Outlooks for 2020 and 2030
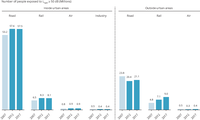
Data submited by countries up to 01/01/2019

Data submited by countries up to 01/01/2019

Different scales between the two figures. No data available for Liechtenstein and Switzerland. Emissions reported by Czechia, Cyprus, Malta and the Netherlands are close to zero, and Turkey reported zero PCB emissions.

The figure shows the landfilling rate for municipal waste by country. Each dot represents a country. The boxes represent the upper and lower quartiles, and the line in the box shows the median.