
The map shows the results of classification of Eutrophication Status using the HEAT+ tool. Eutrophication status is classified as ‘non-problem areas’ or ‘problem areas’.
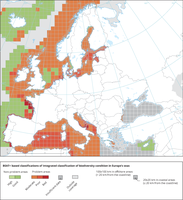
The map identifies problem vs. non-problem areas for biodiversity in Europe's seas by identifying the worst case index value calculated by the BEAT+ tool for those biodiversity components where indicators were available.
The status is evaluated in five classes, where High and Good are recognised as ‘non-problem areas’ and Moderate, Poor and Bad are recognised as ‘problem areas’

The map shows the loss and gain of forests aggregated in a 10 km grid. Units are in ha/km2.
The following CLC classes were used:
Consumption of transitional woodland (LCF71),
Consumption caused by forest and shrub fires (LCF92),
Consumption caused by forest management (LCF74),
Afforestation (LCF72),
Forest-internal conversion (LCF71, LCF73 and part of LCF74),
Withdrawal of farming with woodland creation (LCF61),
Total formation of forest.
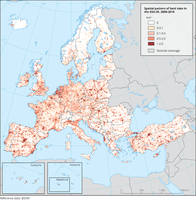
Land take as a result of urban sprawl is measured from the Copernicus Corine Land Cover dataset between 2000-2018. The map shows for each grid cell the area in km2 which was converted to urban areas. For visualization land take data is presented in a 10km grid. The original data which statistics are derived from is from the 100m spatial resolution CLC dataset series.
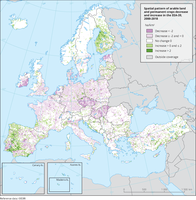
The map shows the loss and gain of arable land and permanent crops aggregated in a 10 km grid.
The following CLC classes were used:
211 Non-irrigated arable land,
212 Permanently irrigated land,
213 Rice fields,
221 Vineyards,
222 Fruit trees and berry plantations,
223 Olive groves,
241 Annual crops associated with permanent crops.

Yearly vegetation productivity during 2000-2016 are analyzed in areas under drought pressure, measured as precipitation shortages and low soil moisture content. Vegetation productivity values are disaggregated and detailed by year and by detailed land cover categories. Strong negative values indicate strong drought intensity, with vegetation productivity values lower than the long term average normal condition.
Scroll down to the More information section for further details.
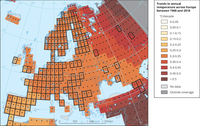
Boxes outlined in solid black contain at least three stations and so are likely to be more representative of the grid. A significant (at the 5 % level) long-term trend is shown by a black dot.
Stations available in the European Climate Assessment and Datasets (ECA&D) (with different lengths of records) for daily maximum and minimum temperature.
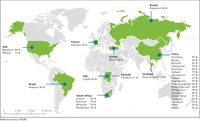
Contribution of primary global suppliers of critical raw materials, average from 2010 to 2014
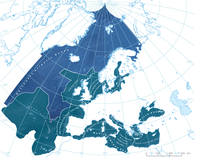
The HRL Small Woody Features (SWF) is a new CLMS product, which provides harmonized information on linear structures such as hedgerows, as well as patches (200 m² ≤ area ≤ 5000 m²) of woody features across the EEA39 countries.
Map of marine regions and subregions in the EU, including their acronyms.

The map describes combined effects index values for pressures caused by land-based human activities. The relative values indicate areas where the pressures potentially affect the marine ecosystem. The table shows the frequency of assessment units indicating pressure

The map describes the combined effects index values for pressures on marine species and habitats in Europe's seas. The relative values indicate areas where the pressures potentially affect the marine ecosystem. The table shows the spatial coverage of the sea-based pressures in three marine zones
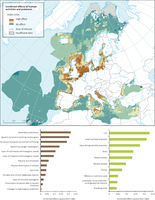
The map describes combined effects index values for pressures caused by human activities. The relative values indicate areas where the pressures potentially affect the marine ecosystem.
The charts shows the ranking of key groups of pressures causing ecosystem effects and ecosystem components being affected by them in Europe’s seas
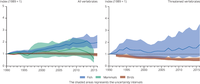
The Living Planet Index (LPI) is used for a number of biodiversity indicators, based on geometric averaging.

This figure summarises the level of threat for species in different biodiversity groups based on their current status or population trends (where known). The data was extracted from a range of IUCN Red List sources, primarily reports developed with EEA & European Commission specifically for European populations.

The figure shows the overall summary of the state and trends in European marine biodiversity trends & status assessed by Regional Seas Conventions (RSCs) and European assessments. Where assessments based on limited data or restricted regions, grey colors is used

The figure shows the evolution of the EU blue economy by sector in the period from 2009 to 2018

Results of classification of Ecosystem Health using the MESH+ tool. (MESH+: Marine EcoSystem Healt). Status is evaluated in five classes, where NPAhigh and NPAgood are recognised as ‘non-problem areas’ and PAmoderatne, PApoor and PAbad are recognised as ‘problem areas’
The Water Framework Directive (WFD) reference spatial data sets include information about European river basin districts, river basin district sub-units, surface water bodies, groundwater bodies and monitoring sites used in the first and second River Basin Management Plans (RBMP).
The data sets are part of the Water Information System for Europe (WISE), and compile information reported by the EU Member States, Norway, Iceland and the United Kingdom to the European Commission (EC) and the European Environment Agency (EEA) since 2010.
The raster datasets describe land cover flows between 2000-2018, 2000-2006, 2006-2012 and 2012-2018 for the EEA39 region. Land Cover Flows summarize and interpret the 44x43=1892 possible one-to-one changes between the 44 CORINE land cover classes. The changes are grouped to so called flows of land cover and are classified according to major land use processes. The nomenclature of flows is organized on 3 hierarchical levels. See lineage on the nomenclature.
The classification of land cover flows results from the feasibility studies and subsequent revisions after discussion with experts in agri-environment and forestry. Basically, the classification of land cover flows distinguishes change between broad land cover classes and changes internal to these classes. Analysis of land cover flows supplies a rapid vision of land use change processes taking place and they shed light on the drivers of various land use change processes such as e.g. urbanization.