
The figure illustrates the estimated effects on key air pollutants at the national level, following the increase in renewable energy consumption since 2005
The figure illustrates the estimated effects on national primary energy use of fossil fuels due to the increase in national renewable energy consumption since 2005.

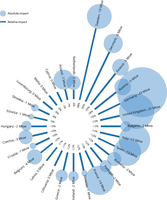
The figure illustrates how much renewable energy consumption has grown per technology and sector by 2018, compared with the corresponding levels in 2005 (EU-28).
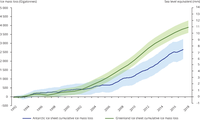
The figure shows the cumulative ice mass loss from the Greenland and Antarctic ice sheets from recent studies, weighted according to the primary satellite data source following the approach of the Ice Sheet Mass Balance Inter-comparison Exercise (The IMBIE team, 2018, doi:10.1038/s41586-018-0179-y; The IMBIE team, 2019, doi:10.1038/s41586-019-1855-2). The shaded uncertainty intervals are estimated from the standard deviation of the individual studies.

Input of impulsive anthropogenic sound was created by combining pulse-block-days (PBD) data from the ICES Registry (for HELCOM and OSPAR areas) and ACCOMBAS (for the Mediterranean Sea).
Electricity generation gives rise to negative impacts on the environment and human health throughout all stages of its life-cycle. To date, power generation remains the largest GHG-emitting sector in Europe. Carbon dioxide (CO2) is by far the most commonly-emitted GHG across the sector, being a product of combustion processes. An almost complete decarbonisation of the EU’s electricity sector is needed in order to meet the EU’s objective of becoming the first carbon-neutral continent by 2050.
Electricity can play an increasing role in decarbonising energy use across a number of sectors, such as transport, industry and households. Information about the carbon intensity of electricity generation is therefore relevant for many stakeholders. The EEA and its European Topic Centre for Climate Change Mitigation and Energy (ETC/CME) produce each year country- and EU-level data on the average annual CO2 emission intensity of electricity generation.

These maps present a story about how Europe might be affected by key climate hazards such as droughts, floods, forest fires and sea level rise during the 21st century and beyond. These maps are based on different greenhouse gas emissions scenarios and climate models and have been published already in various EEA reports and indicators.

Designation types describe and classify the legal instruments or other effective means used to achieve the long-term conservation of nature in protected or other conserved areas. European countries designate protected areas under sub-national, national and EU legislation as well as under international conventions and agreements.
The designation types are classified according to three categories (A, B and C) that are linked to the definitions of protected areas and other conserved areas under “other effective area-based conservation measures” (OECMs).
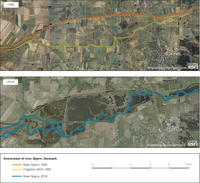
A case study example of floodplain habitat change following the first drainage and straightening, and the later restoration of a river in western Denmark. The River Skjern was channelised in 1968 and in 1999-2003 the river was restaurated. The orthophoto mosaics shows the situation before the restauration (1992) and after (2018).
Copernicus analyses of total ozone column over the Antarctic. The blue colours indicate lowest ozone columns, while yellow and red indicate higher ozone columns. Ozone columns are commonly measured in Dobson Units. One Dobson Unit is the number of molecules of ozone that would be required to create a layer of pure ozone 0.01 millimetres thick at a temperature of 0 degrees Celsius and a pressure of 1 atmosphere. 300 DU corresponds to 3 millimetres of ozone.
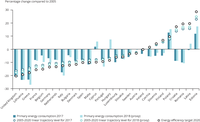
Primary energy consumption and linear trajectory levels to reach 2020 targets, 2017 and 2018.
In accordance with the Energy Efficiency Directive (2012/27/EU), the EU Member States have set up national indicative targets that, collectively, should help the EU to reach its 20 % energy efficiency target by 2020. This graph show which countries are in line with, below or above their linear trajectories
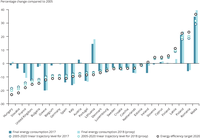
In accordance with the Energy Efficiency Directive (2012/27/EU), the EU Member States have set up national indicative targets that, collectively, should help the EU to reach its 20 % energy efficiency target by 2020. This graph show which countries are in line with, below or above their linear trajectories (2017 and 2018)