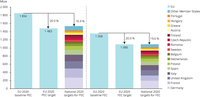
Taken together the figure shows that the sum of all individual 2020 targets from Member States’ for their primary energy consumption add up to an overall EU level which remains 3 % higher than the target defined for the EU under the Energy Efficiency Directive (EED). For final energy consumption, the sum of Member States individual targets is by 0.3 % higher than the reduction level defined in the EED.

The bar chart shows the change in gross final energy consumption (both total and from renewables sources) and renewable energy share for the EU Member States.

This map depicts the Elbe river basin land cover within Germany and the locations of German Elbe authorities.
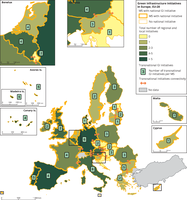
The map shows the Reported green infrastructure (GI) initiatives across EU-28 by Member State (MS), 2015.

Food system actors represent the largest group of natural resource managers in the world. They
are critical in both creating the problems and implementing the solutions. Identifying actors along
the food chain as well as where and how power is located enables policy makers to develop
management approaches targeted towards those actors with influence. In addition to those
directly involved in food chain activities, governments and civil society are also important as they
set the wider policy and societal context.
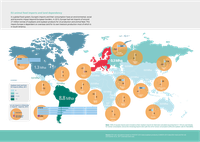
In a global food system, Europe’s imports and their consumption have an environmental, social
and economic impact beyond European borders. In 2013, Europe had net imports of around
27 million tonnes of soybeans and soybean products for oil production and animal feed. This
means Europe is dependent on overseas land for its own livestock production most of which is
in South America.

In the EU today, 5 of the 7 biggest risk factors for premature death – blood pressure,
cholesterol, body mass index, inadequate fruit and vegetable intake and alcohol abuse – are
in part related to how we eat and drink. The average yearly food intake by a European adult is
shown below. In 2014, more than 50% of the European population was overweight, with over
20% classified as obese.
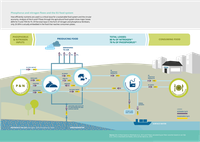
How efficiently nutrients are used is a critical issue for a sustainable food system and the circular
economy. Analysis of the N and P flows through the agricultural food system show major losses
(80% for N and 70% for P). Of the total input in the form of nitrogen and phosphorus fertilisers,
only 20-30% is actually embedded in the food that reaches consumers plates.

The complexity of the food system requires a framework to better understand where and how to act.
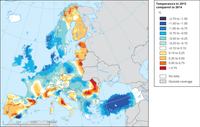
Temperature in 2015 compared to 2014




